Vertical Inline Pumps: Definition, Types, Benefits & Applications
Vertical inline pumps are compact, efficient, and easy-to-maintain solutions for moving fluids. Designed with aligned inlet and outlet ports, they save space and simplify flow, making them ideal for HVAC, water supply, and industrial systems.
What are Vertical Inline Pumps?
Vertical inline pumps feature a design where the suction (inlet) and discharge (outlet) are aligned with each other, with the pump and motor in a vertical configuration. Supported by the piping system, inline pumps minimize the need for complex layouts or extra support structures (Hydraulic Institute).
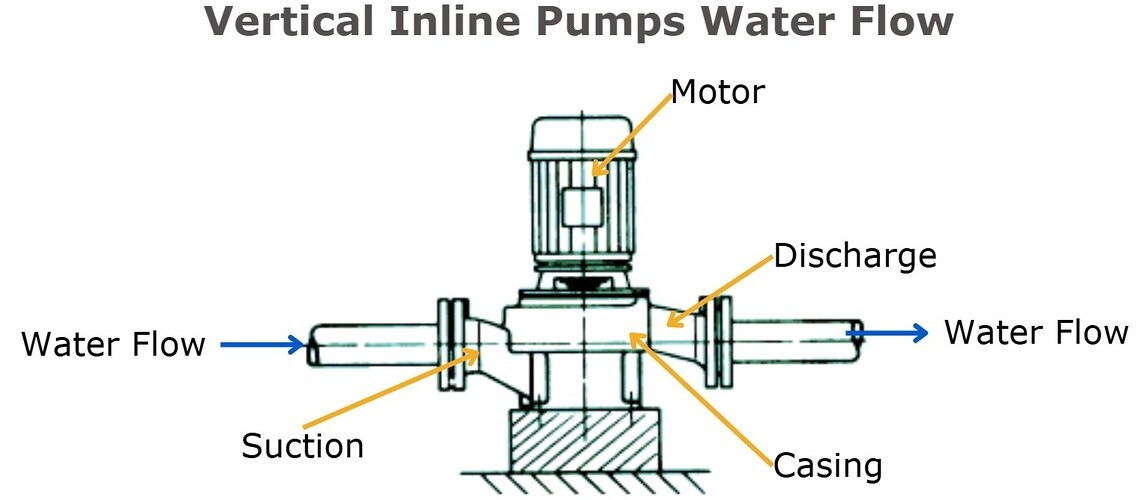
As part of the overhung, centrifugal pump family, inline pumps feature an impeller mounted on the end of a shaft that extends outward, or is “overhung”, from its bearing supports, offering reliable and efficient performance.
Main Components of a Vertical Inline Pump
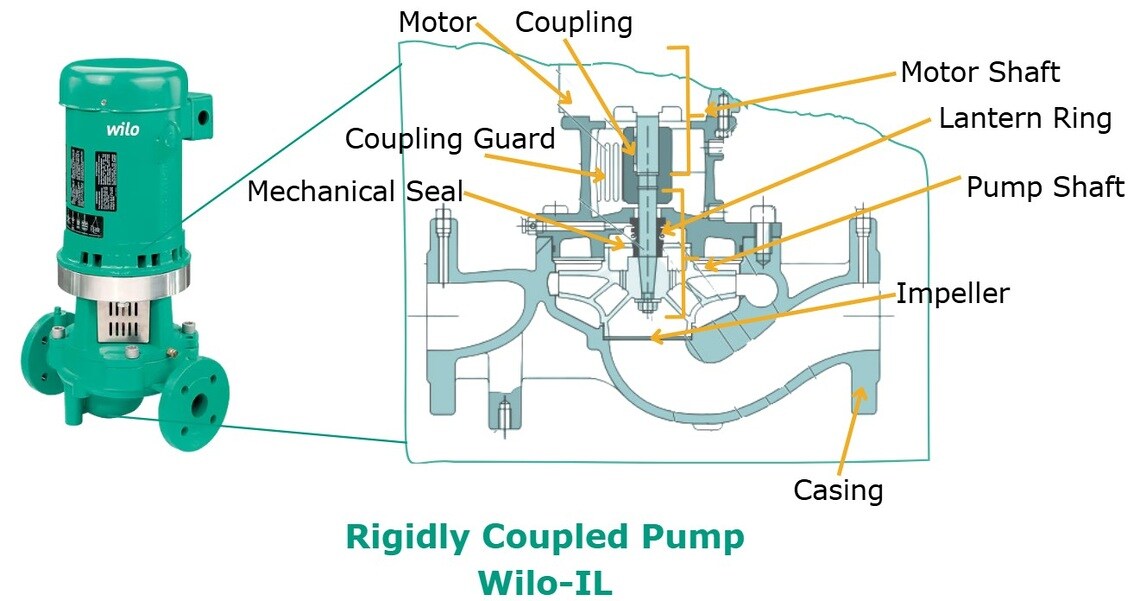
- Casing: Houses the pump's internal parts and directs the flow of fluid, providing pressure containment.
- Impeller: A rotating component that moves the fluid by converting mechanical energy into kinetic energy.
- Shaft: Connects the impeller to the motor, transmitting rotational energy.
- Bearings: Support the shaft and reduce friction during operation.
- Mechanical Seal or Packing: Prevents fluid from leaking along the shaft where it exits the pump casing.
- Motor: Powers the pump by providing rotational energy to the shaft and impeller.
- Suction and Discharge Ports: The inlet (suction) and outlet (discharge) connections for fluid entry and exit, aligned in a straight line.
Operating Principle
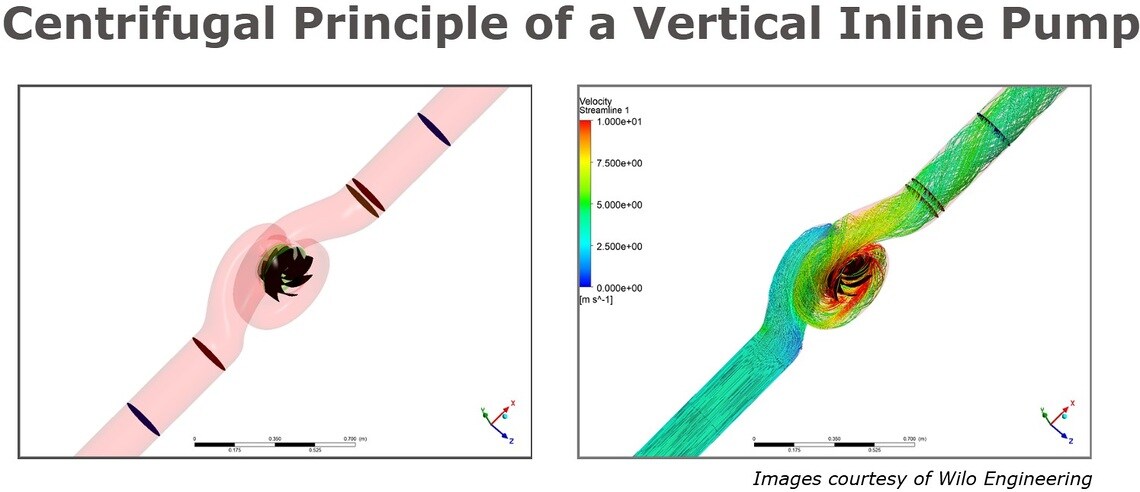
Like all centrifugal pumps, vertical inline pumps operate based on the principle of centrifugal force. In a vertical inline pump, fluid is drawn into the suction inlet and then enters the impeller. As the impeller rotates, it imparts energy to the fluid, causing it to move radially outward, creating a low-pressure area at the eye of the impeller that continuously draws in more fluid. The fluid is then pushed outwards toward the outer edges of the impeller and exits at a higher pressure.
How Vertical Inline Pumps Differ from other Overhung Pumps
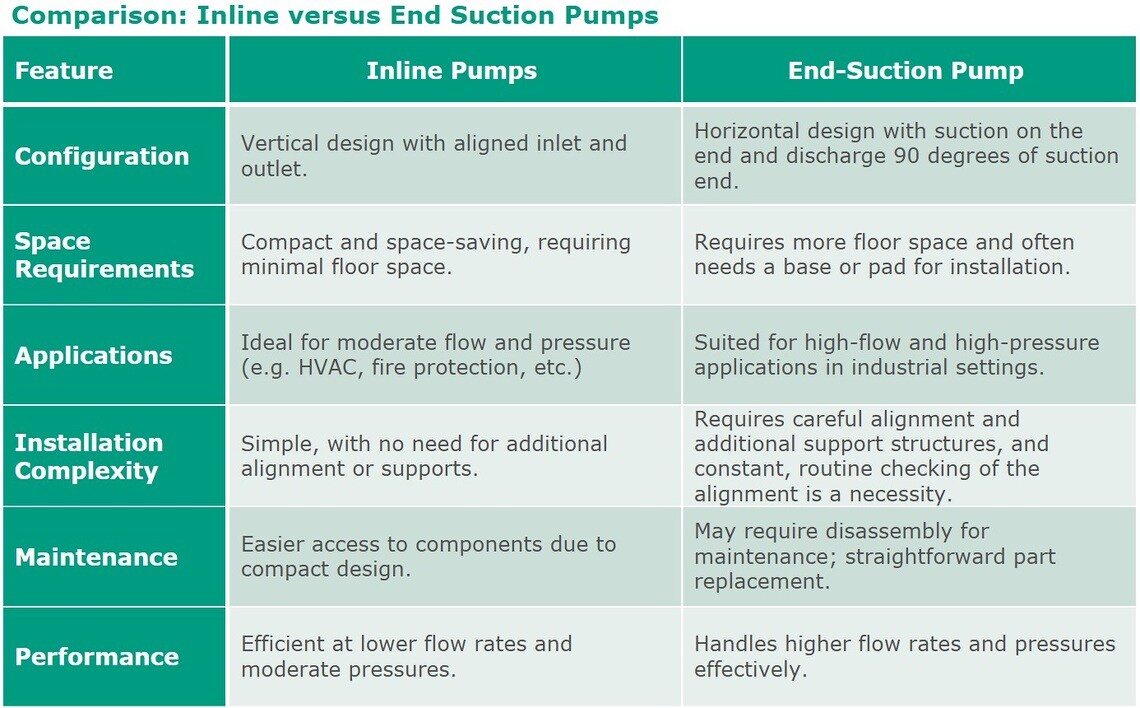
Vertical inline pumps differ from other overhung pumps primarily in their design and space requirements. Unlike traditional overhung pumps, such as end suction pumps which have a suction on one side and a discharge often at a 90-degree angle, while vertical inline pumps are in a straight line. This design allows for a more compact footprint, making vertical inline pumps ideal for applications with limited space.
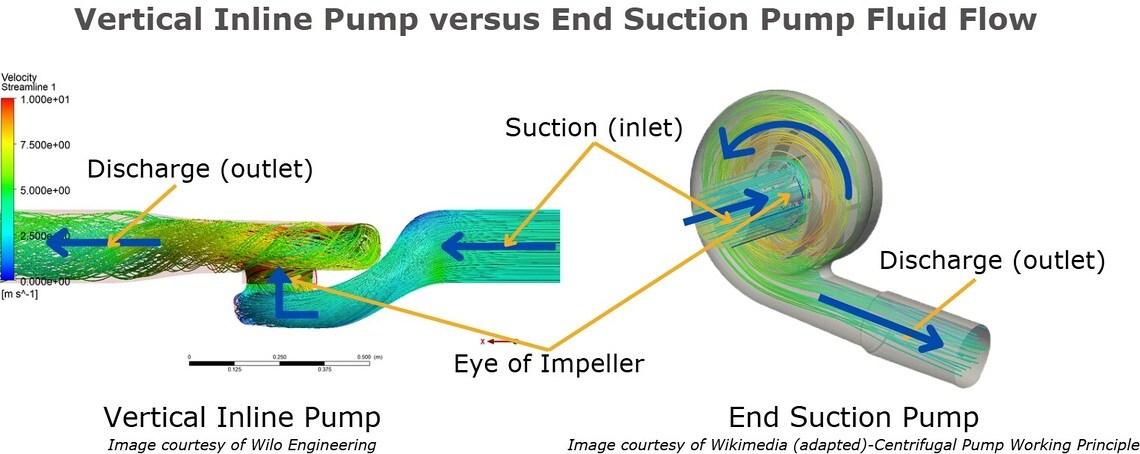
Additionally, their upright configuration may simplify installation within existing piping systems by reducing the need for extensive pipework modifications. While both types are centrifugal pumps, vertical inline pumps provide a direct flow path for the fluid, enhancing efficiency and minimizing directional changes, whereas overhung pumps typically require more space and involve more complex flow redirection.
Vertical inline pumps and circulators share similarities in their compact design and alignment of suction and discharge ports, but they differ in application and performance characteristics. Vertical inline pumps have higher flow and pressure capacity compared to circulators. They are typically larger, more robust, and capable of handling a wide range of fluids, including those with varying temperatures and viscosities.
Circulators, on the other hand, are smaller pumps primarily used in low-pressure applications, such as circulating water in heating, cooling, or domestic hot water systems. They are optimized for energy efficiency and simplicity in residential and light commercial settings, whereas vertical inline pumps are more versatile and suitable for demanding, large-scale operations. Circulator pumps also differ by having horizontal motors.

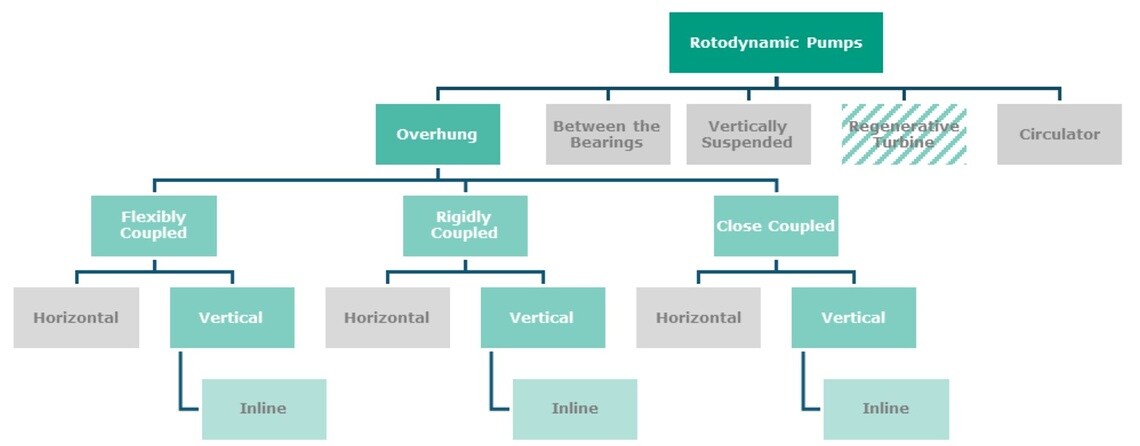
Types of Vertical Inline Pumps:
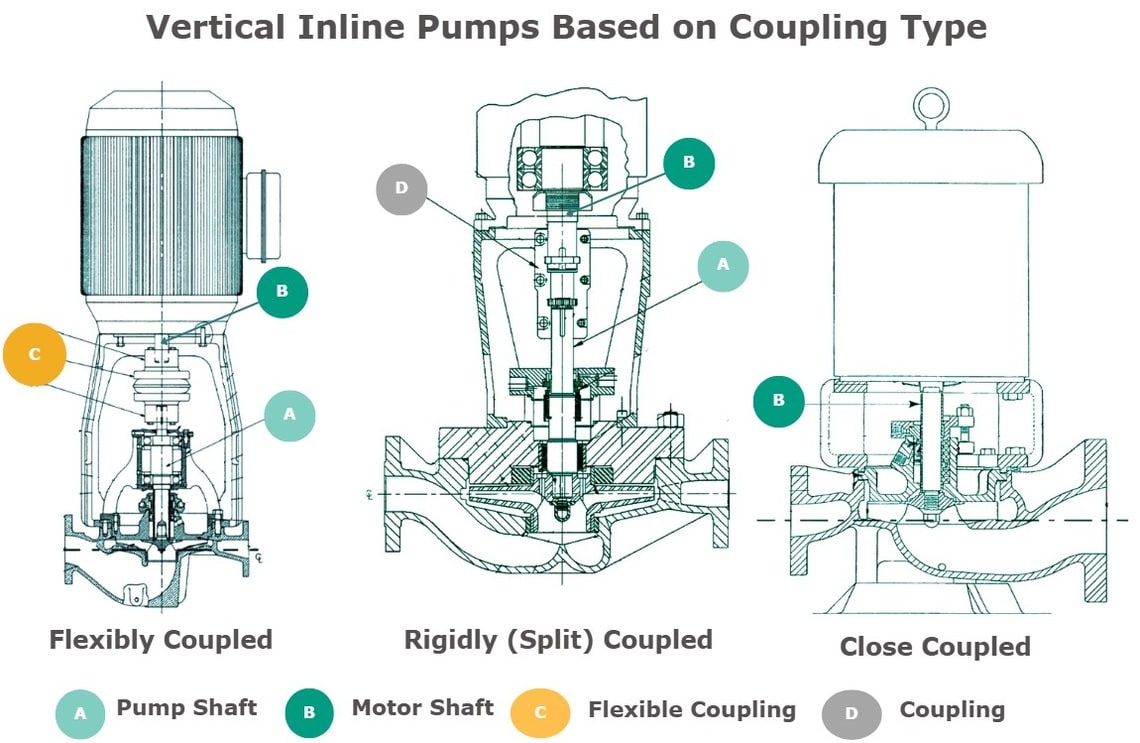
Vertical inline pumps are classified based on their coupling method. Coupling refers to how the pumps and its driver (motor) are connected. Coupling type affects alignment, maintenance, space requirements, and the overall performance of the pump.
- Flexibly Coupled: In this design, the pump and motor shafts are connected by a flexible coupling that accommodates slight misalignment. This type allows for easier maintenance of internal components without disconnecting the pipework, although it is less common than other configurations.
- Rigidly Coupled: In a rigidly (or short, split coupled) coupled pump, the pump and motor are connected by a rigid coupling that does not allow for any movement or misalignment between them and the motor bearings carry all the thrust loads generated by the impeller.
- Close Coupled: In a close coupled pump, the pump and motor are mounted together in a single unit, thus the pump’s impeller is directly mounted on the motor shaft. This design eliminates the need for a separate coupling or alignment between the pump and motor. Close coupled inline pumps are the most affordable type of vertical inline pump.
Key Applications of Vertical Inline Pumps
Vertical inline pumps are suitable for applications where a compact design is required or where space is limited. Typical applications can therefore be found in building services engineering: in larger air conditioning systems, heating systems, and water circulation systems. However, vertical inline pumps are also used for process applications in industry.
- HVAC Systems: Circulation in heating and cooling systems.
- Fire Protection: Reliable performance in fire suppression systems.
- Water Supply and Distribution: Ensuring steady flow in municipal and industrial settings.
- Industrial Processes: Suitable for chemical, pharmaceutical, thermal plant, and data center applications.
Advantages of Vertical Inline Pumps
Vertical inline pumps are compact, efficient, and easy to maintain, making them ideal for space-limited installations in urban and industrial settings. Their aligned suction and discharge ports simplify piping layouts, reduce pressure losses, and lower installation costs. Designed for moderate flow rates and versatile applications, they handle a wide range of temperatures and pressures.
- Space Efficiency: Ideal for tight installations.
- Simplified Maintenance: Components are accessible, reducing downtime.
- Operational Efficiency: High efficiency at lower flow rates.
- Versatility: Handles a range of temperatures and pressures.
Conclusion
Vertical inline pumps are compact, efficient solutions for a wide array of applications. Their straightforward design, combined with operational flexibility, makes them a go-to choice in industries requiring reliable and space-conscious pumping systems. Proper selection and maintenance can significantly enhance performance and lifespan.
Wilo is Your Solutions Provider
Wilo is your trusted solutions provider for cutting-edge pumping and water management systems. With a commitment to innovation, efficiency, and sustainability, Wilo delivers high-performance solutions tailored to meet the needs of diverse industries, from residential and commercial applications to large-scale industrial projects. Our advanced technologies, reliable products, and expert services ensure optimal fluid circulation, energy savings, and environmental responsibility. Whether you need energy-efficient pumps, custom systems, or technical support, Wilo is here to help you achieve your goals with unparalleled precision and reliability. Partner with Wilo and experience the future of fluid management today!
March 2025 | tlk
Featured Products
-

Wilo-Stratos GIGA2.0-I
-
Wilo-CronoLine-IL
-

Wilo-VeroLine-IPL


