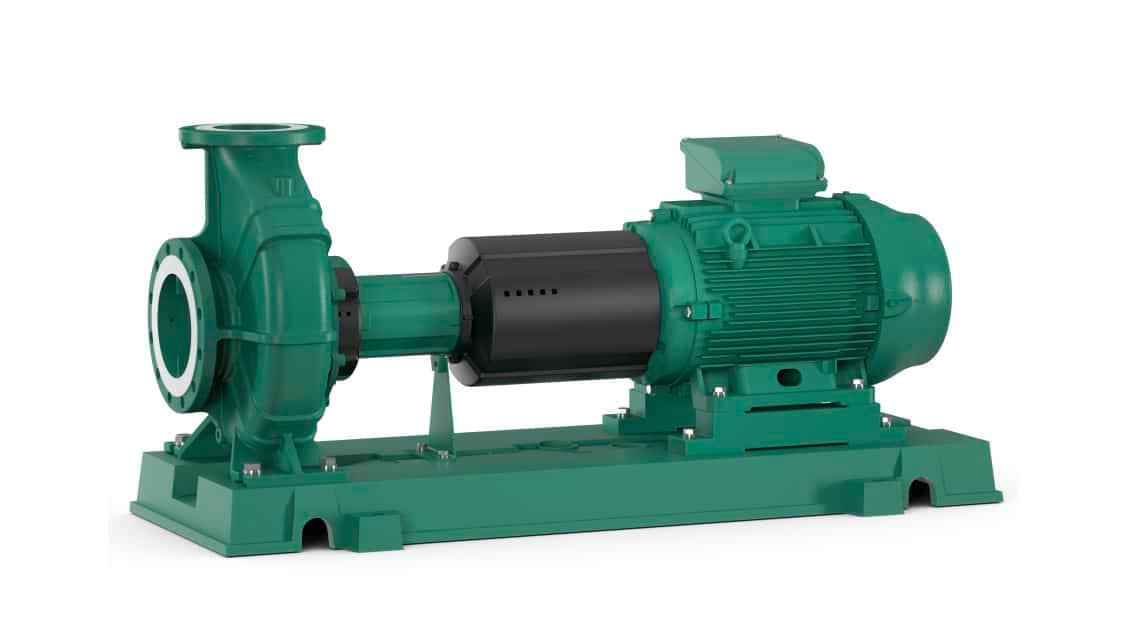
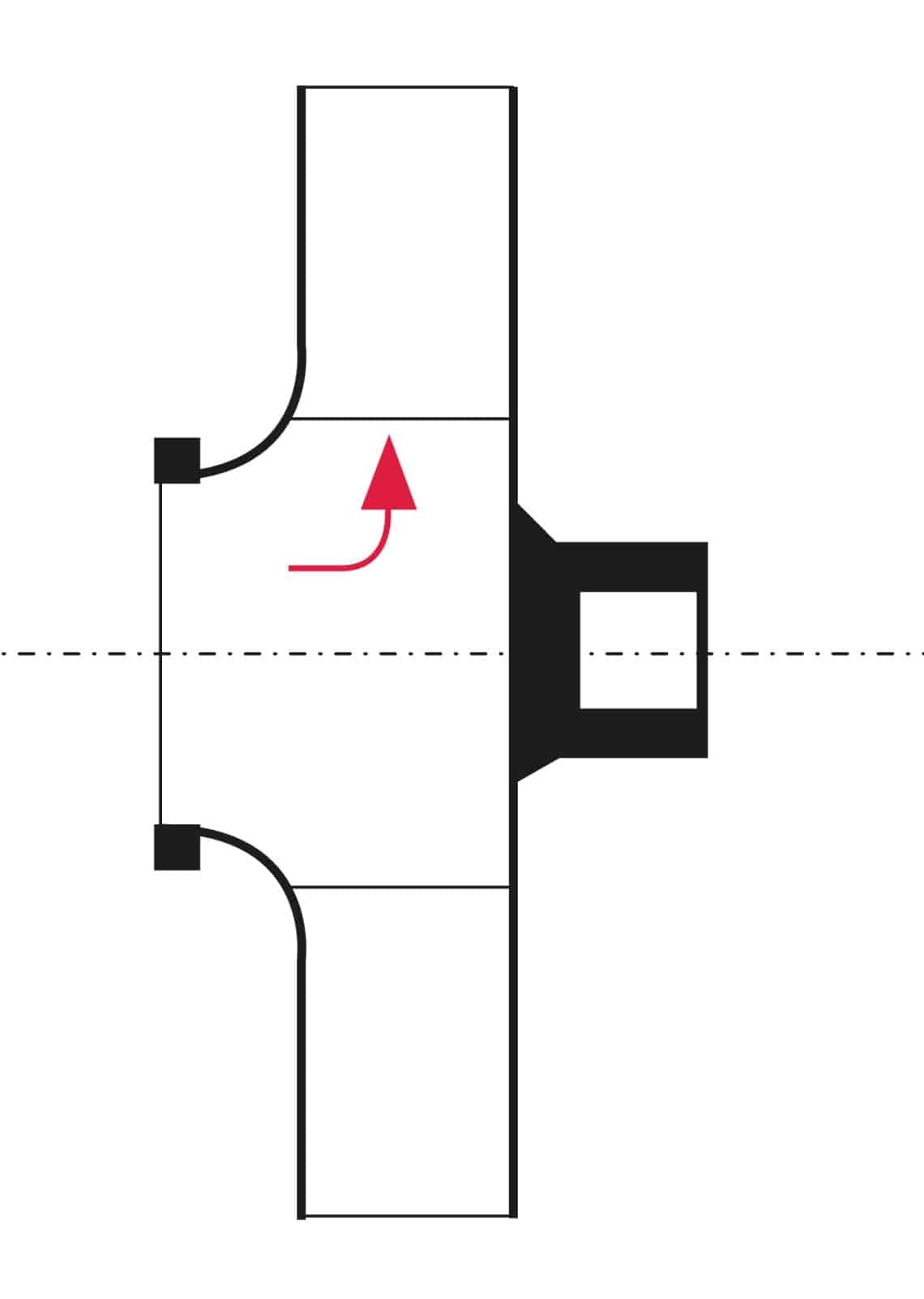
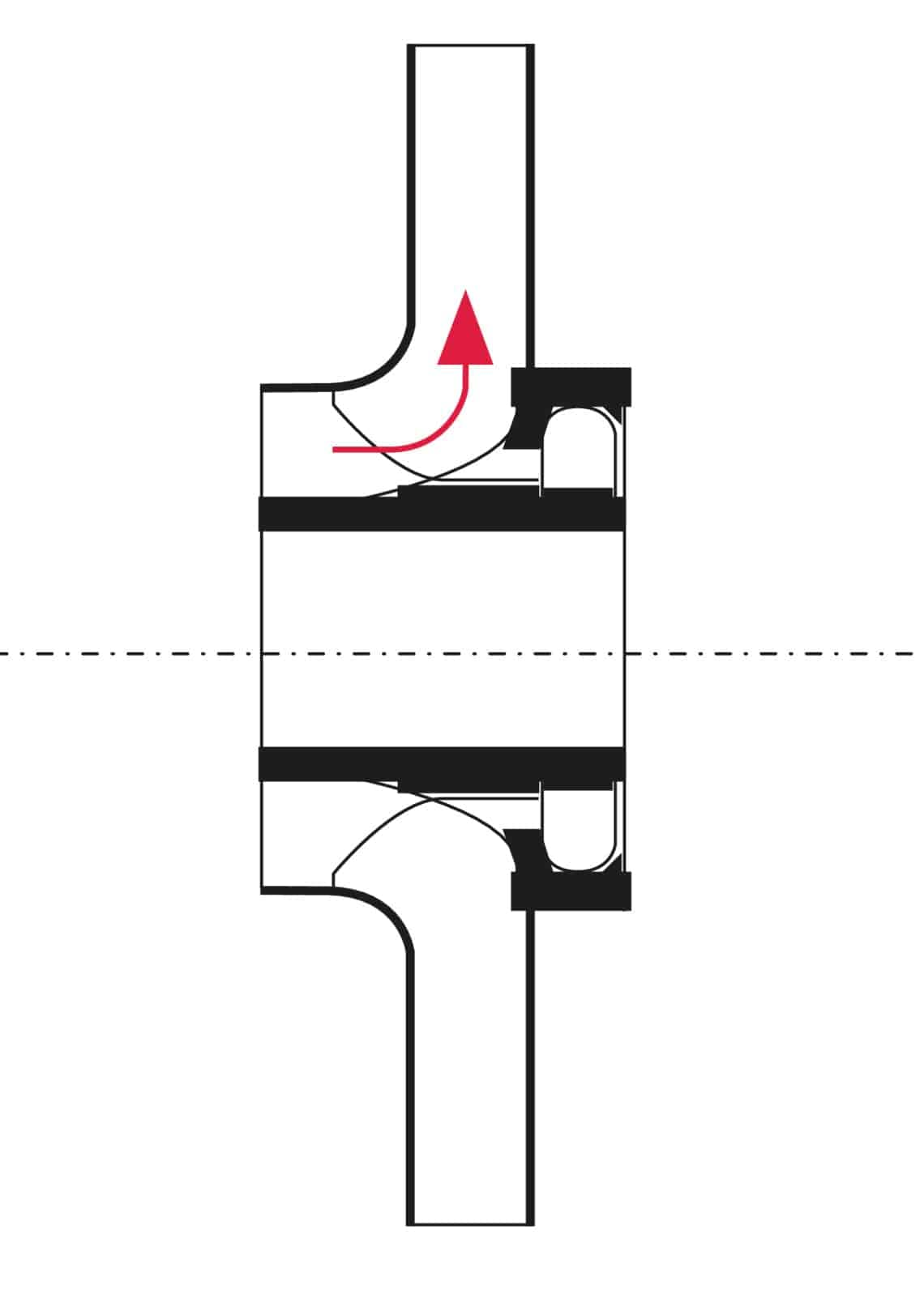
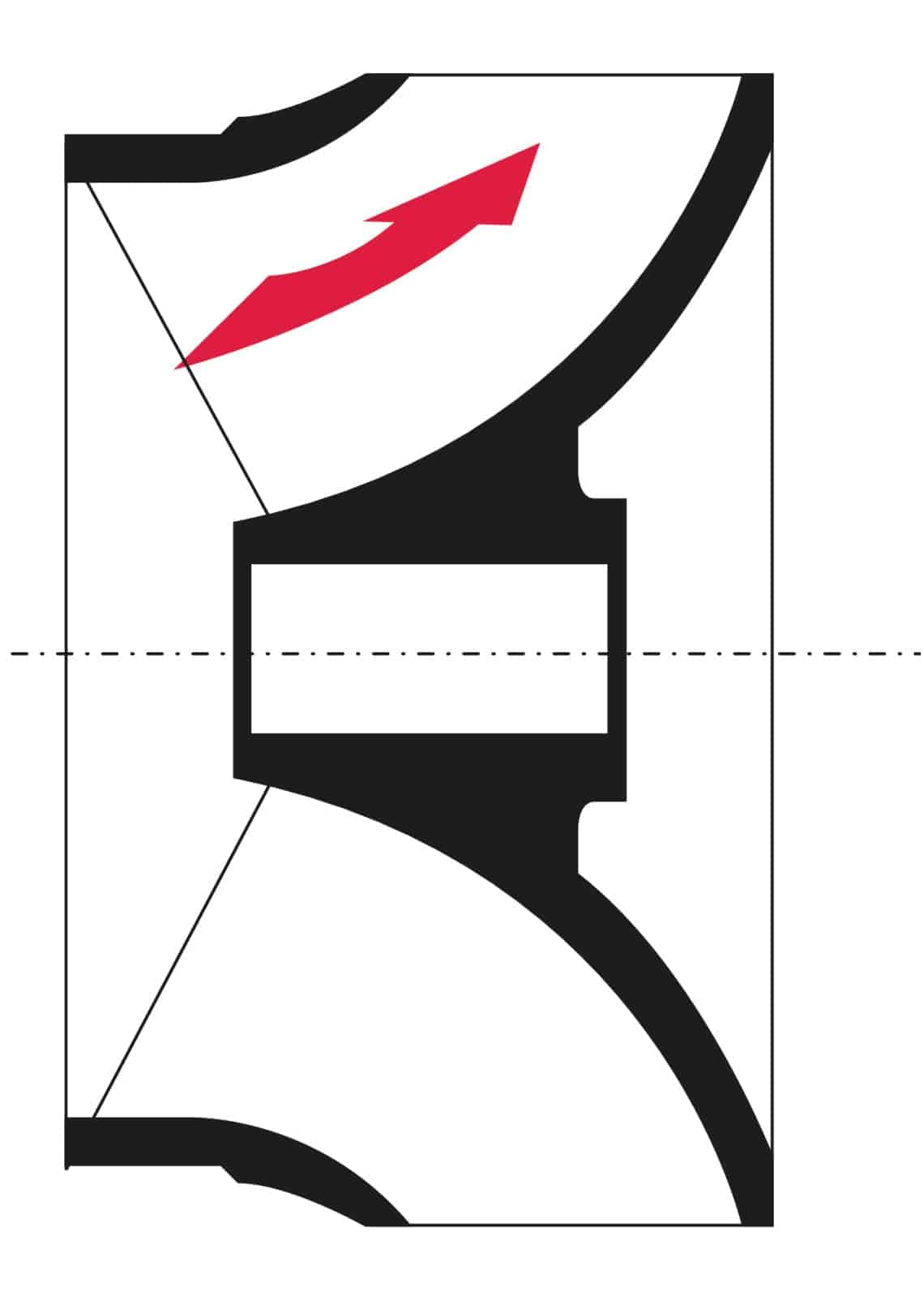
What parts does a centrifugal pump have?
A centrifugal pump consists of the following three main parts:
- motor
- pump housing
- impeller
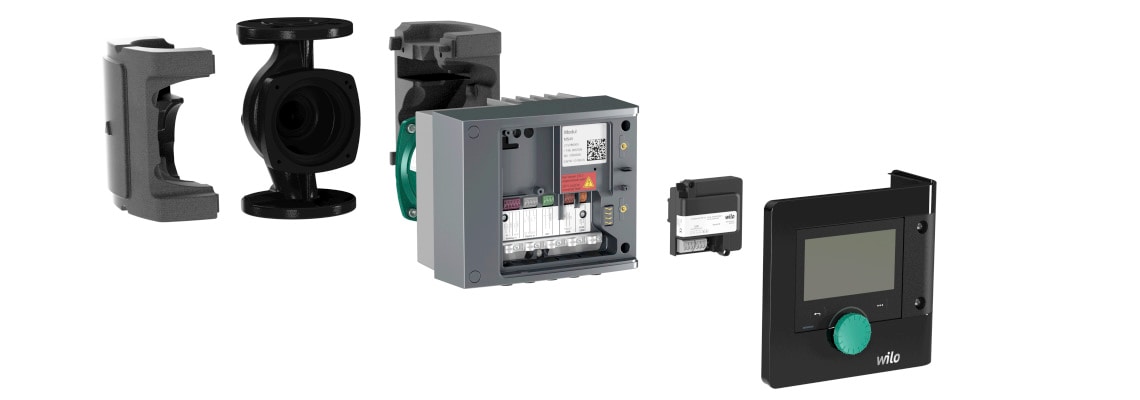

Exploded view Stratos MAXO
Motors for centrifugal pumps
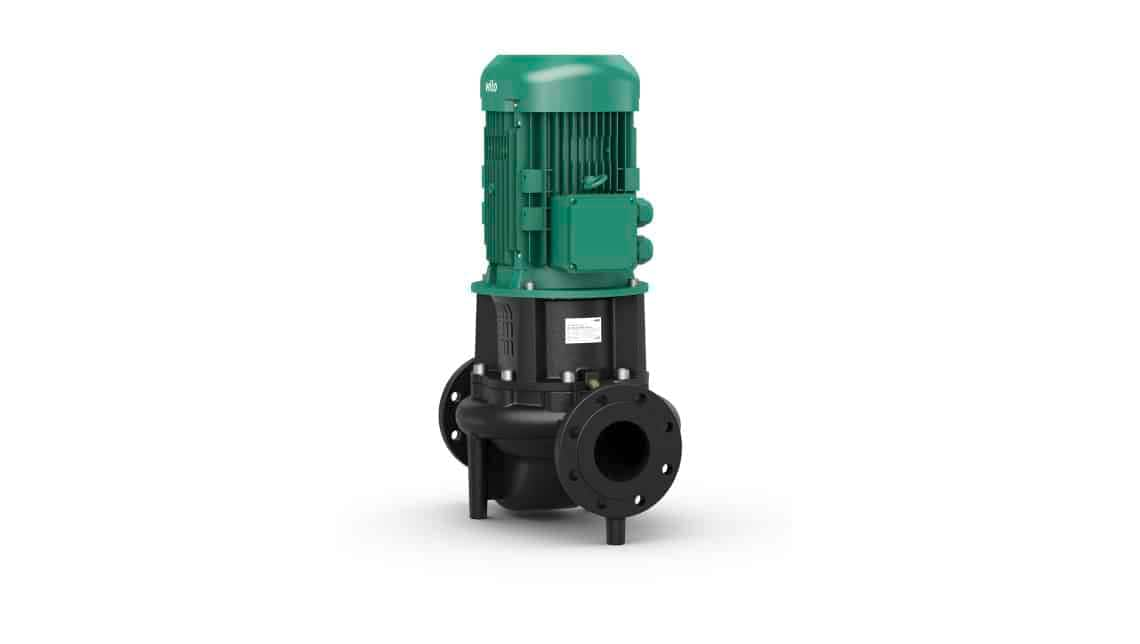
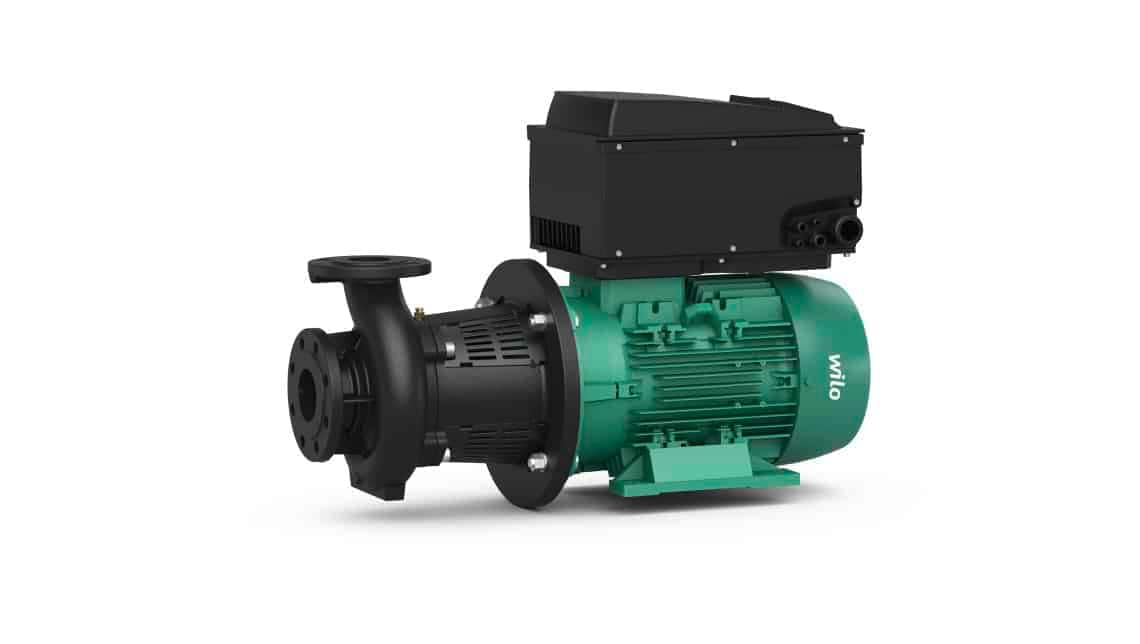
Glanded centrifugal pumps
Glanded centrifugal pumps, also called glanded pumps, are used for pumping large volume flows. Glanded pumps are also better suited than other pumps for pumping cooling water and aggressive fluids. The glanded centrifugal pump is characterised by the air-cooled motor and is fitted with a sliding ring seal (mechanical seal). Unlike glandless pumps, the pumped fluid does not come into contact with the motor; hence the name glanded pump.
Another difference to the glandless pump is the seal of the water-conducting pump housing/shaft towards the atmosphere. This is performed by a stuffing box packing or by a mechanical seal.
The motors of standard glanded pumps are normal three-phase motors with a fixed basic speed. As standard, this is controlled via an external electronic speed change. Today, there are glanded pumps with integrated electronic speed controls, which are available for ever-increasing engine powers due to technical development.
The overall efficiency of glanded pumps is considerably better than that of glandless pumps.
For glanded pumps, the difference is mainly made between these three different design versions:
- in-line pumps
- monobloc pumps
- norm foundation pumps
In-line pumps
If the suction port and discharge port are on one shaft and have the same nominal size, these pumps are called in-line pumps. In-line pumps have an air-cooled and flanged standard motor.
In building services, this construction method has found acceptance for larger capacities. These pumps can be installed directly in the intermediate pipes. Either the pipe is collected by consoles or the pump is mounted on a foundation or its own bracket.
Monobloc pumps
Monobloc pumps are single-stage low-pressure centrifugal pumps in monobloc construction with a directly flanged air-cooled standard motor. The pump housing has an axial suction opening and a radially positioned discharge opening. The pumps are equipped with angle or motor feet as standard.
Norm foundation pumps
For these centrifugal pumps with axial inlet, the pump, coupling and motor are mounted on a common baseplate and therefore only suitable for mounting on a foundation.
Depending on the pumped fluid and the operating conditions, they are either equipped with a mechanical seal or a stuffing box. The vertical discharge opening determines the nominal size of the pump. The horizontal suction opening is normally larger by one nominal opening value.
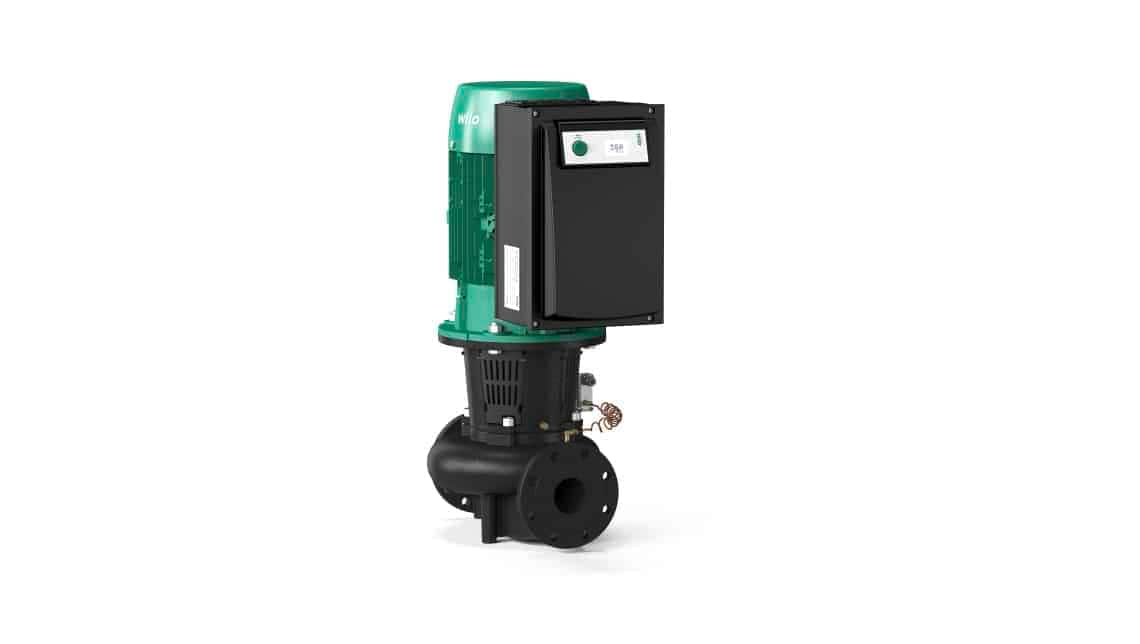
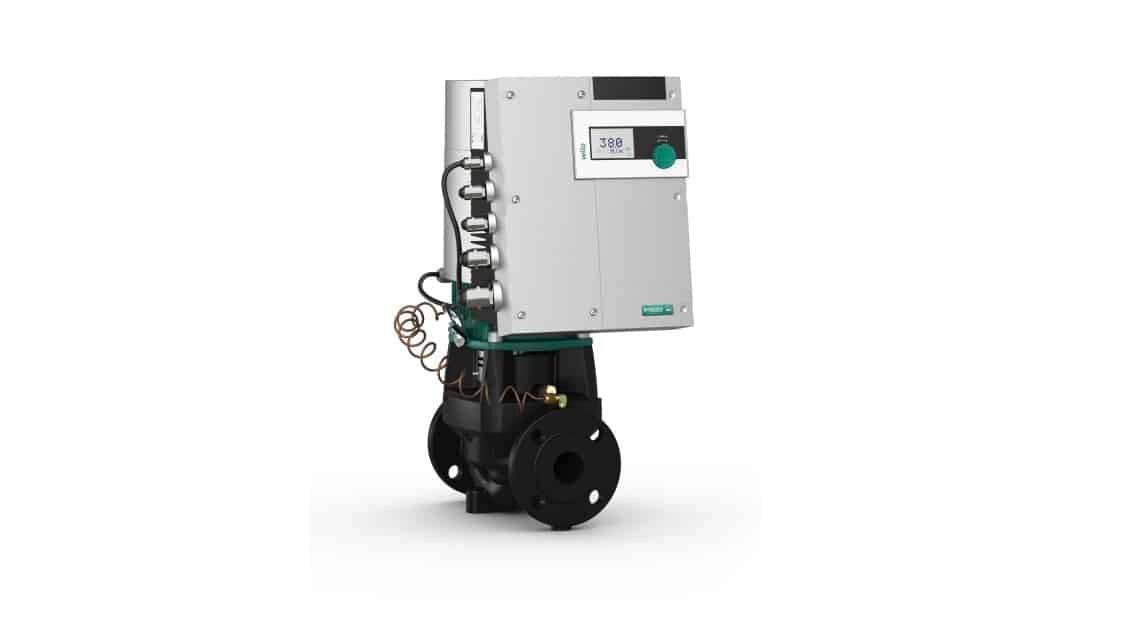
Glandless centrifugal pumps
By installing a glandless pump, optionally in the supply or return pipe, the water is moved very quietly, quickly and intensively. Pipes with small diameters can be used for this, thus reducing the costs of the heating installation. This means that there is considerably less water in the pipes of the heating system. The heating can respond more quickly to changes in temperature and can be better controlled.
The glandless centrifugal pump is characterised by the motor being cooled by the fluid that is pumped.
The impeller of a centrifugal pump is characterised by a radial acceleration of the water. The shaft that drives the impeller is often made of stainless steel; the bearings of this shaft are made of sintered carbon or ceramic material. The rotor of the motor on the shaft runs in the pumped fluid. The water lubricates the bearings and cools the motor.
A can surrounds the current-carrying stator of the motor. It is made of nonmagnetisable stainless steel or carbon fibre and has a wall thickness of 0.1 to 0.3 mm.
For special purposes (e.g. water transport systems), fixed-speed pump motors are used.
For example, if the glandless pump is used in a heating circuit, i.e. to supply the radiators with heat energy, it must adapt to the changing heat demand of the house. Depending on the outside temperature and the external heat, a different amount of added heat is required. The thermostatic radiator valves, which are installed ahead of the heating surfaces, determine the delivery rate.
Glandless pump motors are therefore switched in several speed stages. This speed switching can be performed manually with switches or plugs. Automation is possible through additional external switching and control systems which operate depending on time, differential pressure or temperature.
Since 1988 there have been constructions with integrated electronics that continuously control the speed.
Depending on the size and the required pump capacity, the electrical connection of glandless pumps is carried out with alternating current 1~230 V or with three-phase current 3~400 V. Characteristic for glandless pumps are the quiet operation as well as the missing shaft seal.
The current generation of glandless pumps is constructed according to the modular principle. All modules are variably assembled depending on the pump size and the required pump performance. This makes it easier to repair the pump, if necessary, by replacing certain parts.
An important feature of this construction is the possibility of automatic venting during commissioning.
Premium glandless centrifugal pumps
-
-

Wilo-Stratos MAXO
Standard centrifugal pumps
-

Wilo-Yonos PICO
-

Wilo-Yonos MAXO
Pump housings of centrifugal pumps
In-line pump housings
If the suction port and discharge port are on one shaft and have the same nominal size, these pumps are called in-line pumps.
Monobloc pump housings
The spiral housing has an axial suction port and a radial discharge port. The pumps are equipped with angle or motor feet as standard.
Norm Foundation pump housings
With these centrifugal pumps with axial inlet, the pump, coupling and motor are mounted on a common baseplate and are therefore only suitable for mounting on a foundation.
The vertical discharge opening determines the nominal size of the pump. The horizontal suction opening is normally larger by one nominal opening value.
Impellers in centrifugal pumps
In impeller shapes, a difference is made between open and closed impellers. Today's impeller in most pumps is a 3D construction that combines the advantages of an axial impeller and a radial impeller.
Wilo has the following types of impellers:
- Radial impellers
- Radial 3D impellers
- Semi-axial impellers
- Axial impellers
Most centrifugal pumps on the market have one impeller. There are also many types available that have multiple impellers.
Previous FAQ entry:
How does a centrifugal pump work?Next FAQ entry:
What is the efficiency of a centrifugal pump?We have answers to your questions
Do our products and services interest you? If so, we are happy to help!
Whether you're creating a new project or adjusting service specifications, designing different types of equipment, advising on the selection of pumps and switchgear, or just helping with hydraulic and control issues.
Please contact us - we'd be happy to help.
Find the right contact for your question.